[iOS] Google Promises - delegate, completion handler 보다 간단하게
30 Oct 2019 |
Promises
📌 Index
- Why needed
- What is Promises
- Basics
- creation - pending / resolved
Why needed?
problem
async 처리에서 nested level △▲ readability ▽▼
solution
completion handler 대신 Promise object 를 쓴다.
Example
func data(at url: URL, completion: @escaping (Data?, Error?) -> Void)
func data(at url: URL) -> Promise<Data>
What is a promise?
promise 는 무엇을 대표/표현하는가?
eventual result of an asychronous task, respectively the error reason when the task fails
비동기 task 의 최종적인 결과, 개별적으로 task 실패시의 에러 원인을 나타냄
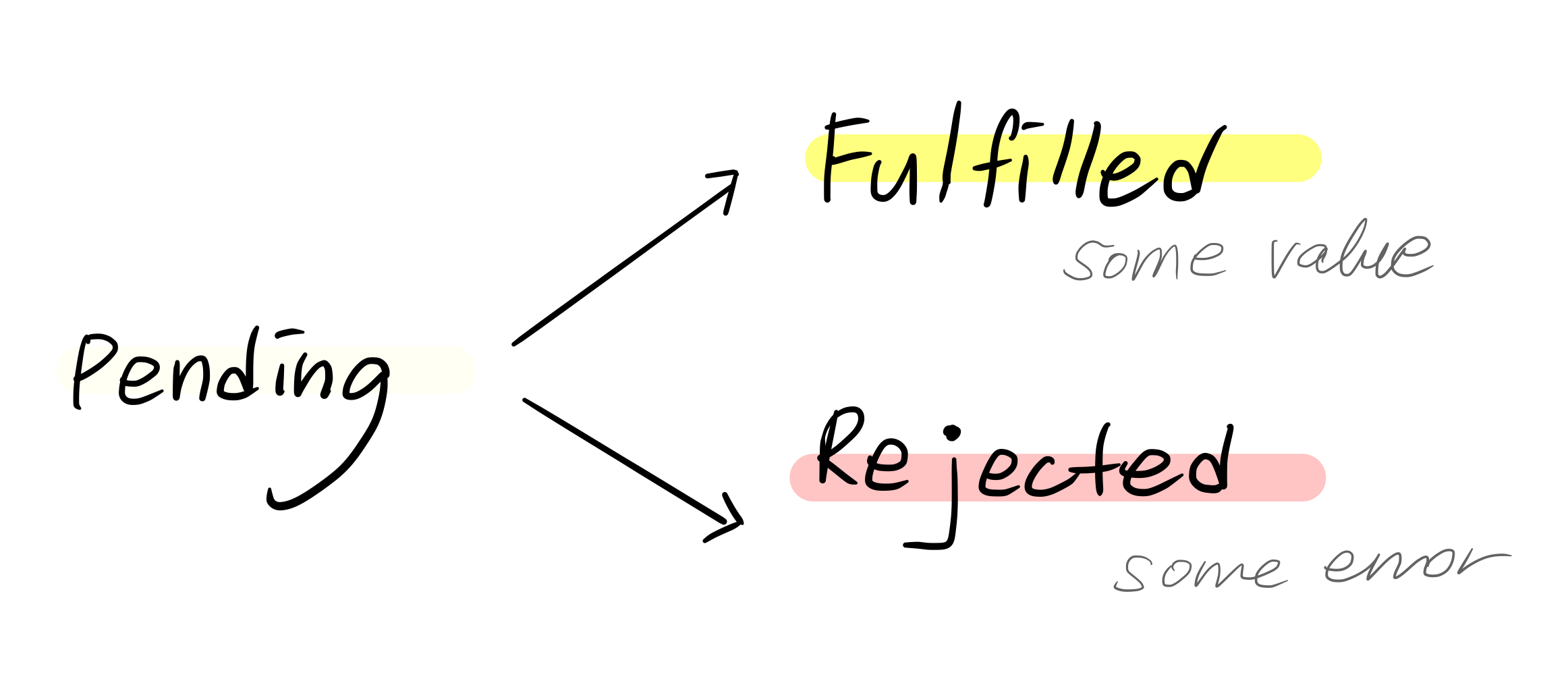
promise 의 3 개의 state
- unresolved
- pending - unresolved, 결과가 not yet available → 아직 completion handler 수행 결과가 나오지 않음
- resolved
- fulfilled - 비동기 처리 결과로 어떤 value가 결정됨
- rejected - 에러로 결정됨
특징
- 한번 fulfilled / rejected 상태가 되면 다시 상태를 바꿀 수 없다
- observer
- infinite(유한)개의 observer 가 promise 가 resolved(결정되기를) 기다리고 있음
- 일단 결정되면 value or error 는 모든 observer 에게 전파(broadcasted) 된다.
- chaining promises
- 각 구독한 promise가 차례로 결정된 value or errror 를 받으면 다시 그 observer 가 새로운 promise 를 생성하는 경우
- chain을 형성할 수 있음.
- 각각의 다른 스레드에서 비동기적으로 value 가 계산됨
- 비동기 task 의 chain 을 형성하기 쉬운 방법
- 다음의 경우 재사용하기 쉬운 코드를 promises 를 통해 구성할 수 있다
- perform a chain of dependent asynchronous operations with one completion block at the end
- have a fall-through behavior for errors to the nearest error handler
- perform many independent asynchronous operations simultaneously with one completion block
- race many asynchronous operations and return the value of the first to complete
- retry asynchronous operations
- and much more
Basics
Promises 생성하기
객체는 pending / resolved(fulfilled, rejected) 두가지 케이스를 생성할 수 있음
pending 을 주로 생성하게 됨
- thread 지정
- default: main thread
- 지정 가능
pipeline
then - observing fulfillment
promise object 가 fulfilled로 결정되어 value를 가지게 될 때, 알림을 받고 싶다면 사용하는 operator
- takes one argument
- a block of code / function (first class citizen)
- another promise object
- value
- error
- void return (not supported, but Promisable can?)
thenoperator 는 void return 을 support 하지 않음- 그래서 wrapper 에서 void를 만든건가?
- 원래 promise 에서 return 할 값이 없다면 nil 혹은 전달받았던 값을 리턴하도록 권장
- then block 이 실행될 custom queue 를 지정할 수도 있음
numberPromise.then(on: backgroundQueue) { number in
return String(number)
}
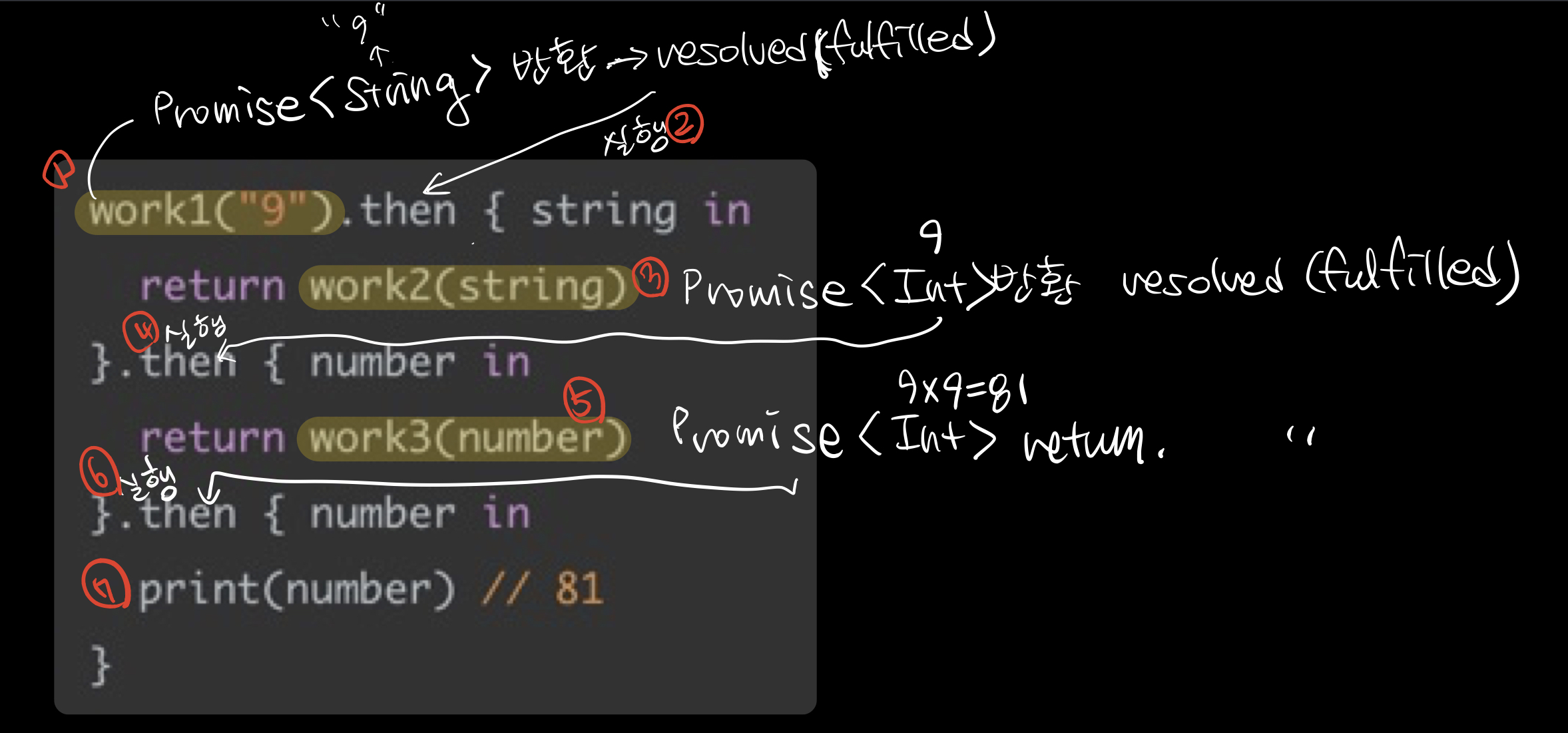
then pipeline
promise 객체 여러개를 함께 파이프라인으로 구성하여 동기 처리처럼 구성할 수 있다
func work1(_ string: String) -> Promise<String> {
return Promise {
return string
}
}
func work2(_ string: String) -> Promise<Int> {
return Promise {
return Int(string) ?? 0
}
}
func work3(_ num: Int) -> Int {
return num * num
}
work1("9").then { string in
return work2(string)
}.then { number in
return work3(number)
}.then { number in
print(number) // 81
}
work1("10").then(work2).then(work3).then { number in
print(number) // 100
}
catch - observing rejection
promise 가 error로 판명날 때 (rejected), 알림을 받고 싶다면 catch operator 를 사용한다
func number(from string: String) throws -> Promise<Int> {
return Int(string) ?? throw Error
}
number(from: "abc").catch { error in
print("Cannot convert string to number: \(error)")
}
catch - pipeline
promise pipeline 에서의 rejection은 파이프라인 아래로 자동으로 넘어가서, 남아있는 then 은 무시된다. 대신에 catch operator 를 실행.
struct CustomError: Error {}
func work1(_ string: String) -> Promise<String> {
return Promise {
return string
}
}
func work2(_ string: String) -> Promise<Int> {
return Promise { () -> Int in
guard let number = Int(string), number > 0 else {
throw CustomError()
}
return number
}
}
func work3(_ number: Int) -> Int {
return number * number
}
work1("abc").then {
return work
}
all - all promises fulfilled
allclass method waits for all the provided promises to be fulfilled
- 모든 promises 가 fulfilled 되면,
all로 return 된 promise 는 모든 fulfilled value 를 담은 array- 하나라도 rejected되면 그 error 를 return
all(
work2("11"),
work2("abc")
).then { eleven, ten in
print(eleven, ten)
}.catch { (error) in
print("error - \(error)")
}
always - fulfill/reject 상관없이 실행되는 곳
alwaysis handy when we want some piece of code to execute always down the promises pipeline, regardless of whether or not the previous promise was fulfilled or rejected.’
any - 일부 reject 이어도 가능
all 과 비슷하지만, 일부가 rejected 되어도 fulfilled 됨
모든 promises 가 rejected -> rejected (OR condition)
- resulting array element :
Maybeenum- two cases :
.value/.error
- two cases :
- any 는 argument 로 최대 3개의 promise 만 받을 수 있음
- 그보다 많은 개수를 사용하고 싶다면 any 안에 any 넣는 식으로 가능
Example
any 안 promise 두개 모두 reject → catch
any 안 promise 한개라도 fulfilled → then
any(
work2("ff"),
work2("abc")
).then { first, second in // Maybe enum type - first, second
if let f = first.value {
print(f)
}
if let s = second.value {
print(s)
}
}.catch { (error) in
print("error - \(error)")
}
await
서로 다른 스레드에서 처리되는 Promise 객체들이 결정되기를 동기로 기다릴수 있음.
- 여러 결과를 비동기로 처리하여 같이 혼합하여 처리해야 되는 경우. then, all 로는 확실하게 pipeline 구성하기 힘든데, 이걸 sync 스타일로 await 로 할 수 있음
delay
같은 value를 fulfill 하는 promise 객체를 주어진 시간 딜레이 이후에 반환함
혹은 같은 error 로 reject 하는 promise 객체를 주어진 시간 딜레이 이후에 반환함
race
all 과 비슷한 class method
recover
error 발생시, promise chain 을 깨지 않고 회복할 수 있는 방법
error 처리 후, 다른 promise 객체로 recover 하도록 처리
getCurrentUserContactsAvatars().recover { error in
print("Fallback to default avatars due to error: \(error)")
return self.getDefaultsAvatars()
}.then { avatars in
self.update(avatars)
}
reduce
retry
처음에 rejected 된 task와 관련된 promise 를 다시 재시도 할 수 있도록 유연성을 제공
- 재시도 횟수
- default : 1회
- rejection 이후 1초 딜레이 이후 재시도
- custom 가능 요소
- custom queue, 재시도 최대 횟수, delay time interval,
- optional predicate(조건) - 조건에 맞지 않은 경우, 횟수가 남아도 early exit 가능
func fetch(_ url: URL) -> Promise<(Data?, URLResponse?)> {
return wrap { handler in
URLSession.shared.dataTask(with: url, completionHandler: handler).resume()
}
}
let url = URL(string: "~~~")
// default - 1초 후 재시도 1회
retry{ fetch(url) }.then { print($0) }.catch{ print($0) s}
// custome queue, 5회 재시도, 2초 딜레이
let customQueue = DispatachQueue(label: "myqueue", qos: .userInitiated)
retry (
on: customQueue,
attempts: 5,
delay: 2,
condition: { remainingAttempts, error in
(error as NSError).code == URLError.notConnectedToInternet.rawValue
}
) {
fetch(url)
}.then { values in
}.catch { error in
}
validate
chain 깨지 않고 value check 하는 방법
Bool value
wrap
handler 사용하여 promise 객체를 만들어주는 class method
retain cycle
promise 의 work block 에서는 strong reference 를 가지지만, 일단 promise 객체가 resolved 되면 observer block 의 reference 를 모두 제거한다.
Void
typealis Void = () // empty tuple